Maximizing Value: 2023 Spring Application of Broiler Litter for Grain Crop Production
Maximizing Value: 2023 Spring Application of Broiler Litter for Grain Crop Production

Spring is here and grain producers across the state are gearing up for planting. One of the many decisions producers have to make before planting is in regard to their nutrient management plan. Broiler litter provides a great opportunity as a complete fertilizer and is being produced and used throughout the state in grain production. However, the value of broiler litter can vary greatly depending on the management practices, nutrient content of the litter, soil test data and commercial fertilizer prices.
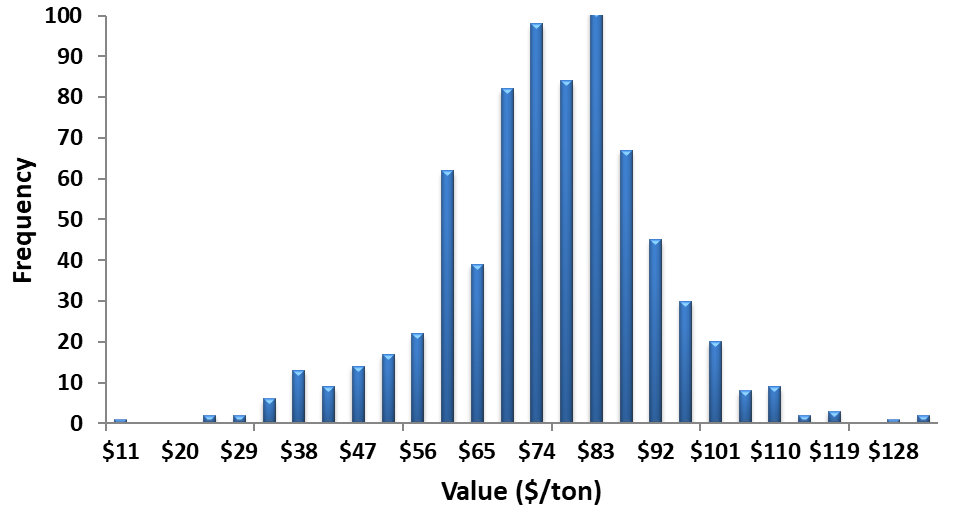
Spring application of broiler litter maximizes plant available nitrogen resulting in the maximum economic value of broiler litter. As mentioned in previous issues, the average nutrient content of a ton of broiler litter in Kentucky (as received) is 50 lbs of nitrogen, 56 lbs of phosphorous, and 47 lbs of potassium. In addition to three macronutrients, broiler litter contains other beneficial elements such as micronutrients (zinc and copper), other secondary macronutrients (calcium carbonate, magnesium, and sulfur), and organic matter which are difficult to quantify in value. For this analysis, the three primary macronutrients (N, P2O5, and K2O) will be used to determine the value of broiler litter. If your soil test recommendations supported the application of broiler litter and you applied or plan on applying this spring, that is equivalent to 50% commercial nitrogen, 80% commercial phosphorous and 100% commercial potassium per ton of broiler litter (as received). Therefore, the nutrients that would be available to the crop from an average ton of broiler litter in Kentucky would be 25 lbs of nitrogen, 45 lbs of phosphorous, and 47 lbs of potassium. With current fertilizer prices of $638/ton for Urea ($0.69/lb N), $825/ton for DAP ($0.63/lb P2O5), $655/ton for potash ($0.55/lb K2O), and $13.50/ton for lime (at the quarry), the average expected value of broiler litter is $73/ton. Therefore, if you can buy broiler litter and have it delivered and spread for less than $73/ton this Spring, broiler litter is a better economic option than commercial fertilizer. Last year, with considerably higher fertilizer prices, the nutrient value of an average ton of broiler litter was $80/ton. But remember, broiler litter nutrient content will vary (see max and min values in Table 1). Figure 1 applies current fertilizer prices to each broiler litter sample submitted for analysis to illustrate the range and frequency in the value of a ton of broiler litter. Given the wide range in value, make sure you measure broiler litter for nutrient content to understand what you are receiving and avoid the risk of overpaying for broiler litter.
Table 1: Sample statistics for the nutrient content of broiler litter samples (n=740)
Figure 1: Variation in value of broiler litter samples given current commercial fertilizer prices and 50% N, 80%P2O5, and 100% K2O plant available nutrients (n=740)
Since the value of broiler litter is dynamic and always changing, a decision tool, "Economic Value of Poultry Litter: Grain Crops, is available so grain producers can enter soil test data, nutrient content of measured litter, commercial fertilizer prices, and management practices to determine the value of boiler litter.
Recommended Citation Format:
Shockley, J. "Maximizing Value: 2023 Spring Application of Broiler Litter for Grain Crop Production." Economic and Policy Update (23):3, Department of Agricultural Economics, University of Kentucky, March 30th, 2023.
Author(s) Contact Information:
