Understanding ESG and Its Impact on Agriculture
Understanding ESG and Its Impact on Agriculture

As companies continue their quest to mitigate their carbon footprint, achieving a “net-zero” goal is one slice of their sustainability pursuit. There are three main factors that are used to assess the sustainability and ethical impact of a company’s operation. These three factors are referred to by their acronym “ESG,” or Environmental, Social, and Governance. In recent years, ESG has become a critical concept in business, influencing how companies operate, make decisions, and engage with communities. While ESG may seem like a concept reserved for large corporations or financial investors, it’s becoming increasingly relevant to all sectors, including agriculture. So, what does Environmental, Social, and Governance mean for corporations, and what elements are considered under each initiative?
Environmental (E): The environmental aspect focuses on how the company impacts the planet. This includes a wide range of issues, from how the business sources raw materials to its carbon footprint and waste management. For example, a company may invest in renewable energy, like wind energy, to operate their facilities. In agriculture, a company may source climate-smart corn and soybeans to reduce the carbon footprint of their raw inputs.
Social (S): The social factor of ESG examines how companies manage relationships with people along their supply chain, employees, customers, and community members. Labor rights, fair wages, safe working conditions, community engagement, and customer satisfaction are elements of social responsibility.
Governance (G): Governance refers to how a company is run. Leadership structure, ethical practices, and compliance with rules and regulations are critical elements in how decisions are made within the business. Accountability and transparency are required for stakeholder trust and the long-term sustainability of the organization.
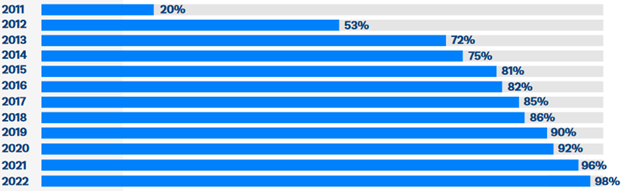
Figure 1 below illustrates that almost all the S&P 500® reported on their sustainability efforts in 2022. While ESG reporting will look and be named differently across each company, the overall goal is the same: communicate their ESG efforts to stakeholders. Example reports can be found below.
Consumer demand, investment appeal, reducing the company’s risk profile, and international trade are reasons why companies are pursuing the above initiatives. So why should farmers in Kentucky care? Understanding corporate ESG initiatives, especially the “E,” helps explain why companies are seeking “net-zero” goals. These “net-zero” goals are what is driving carbon markets in agriculture. Whether it is the development of the carbon offset market for businesses outside of agriculture or carbon insets where companies are looking to source climate-smart commodities, both approaches pose financial opportunities and risks in agriculture (learn more about carbon offsets and insets here). Stay tuned for more resources on ESG, carbon markets, and the announcement of an upcoming webinar title “Preparing Farmers and Ranchers for the Evolution of Carbon Markets.”
Figure 1. Percent of S&P 500® companies that have sustainability reporting
Recommended Citation Format:
Shockley, J. "Understanding ESG and Its Impact on Agriculture." Economic and Policy Update (24):9, Department of Agricultural Economics, University of Kentucky, September 27, 2024.
Author(s) Contact Information:
